The Power of Predictive Maintenance: Reducing Downtime and Costs
- R Praveen

- Jul 15, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: May 16, 2025
Author: R Praveen
Associate Data Consultant, Fluidata Analytics

Over the past few years, companies have been focusing on leveraging their data to drive business insights. Internet of Things (IoT) and sensors generate valuable information that can be used to reduce downtime and the costs associated with it. This can prove to be vital considering that 82% of companies have experienced at least one unplanned downtime incident over the past three years. Unplanned downtime costs as much as $50 billion a year to industrial manufacturers.
Here’s what you’ll find in this article:
The Evolution of Maintenance Strategies
Companies aiming to reduce downtime have been implementing different maintenance strategies, which have evolved over time. These strategies can be categorized into reactive, preventive, or predictive maintenance.
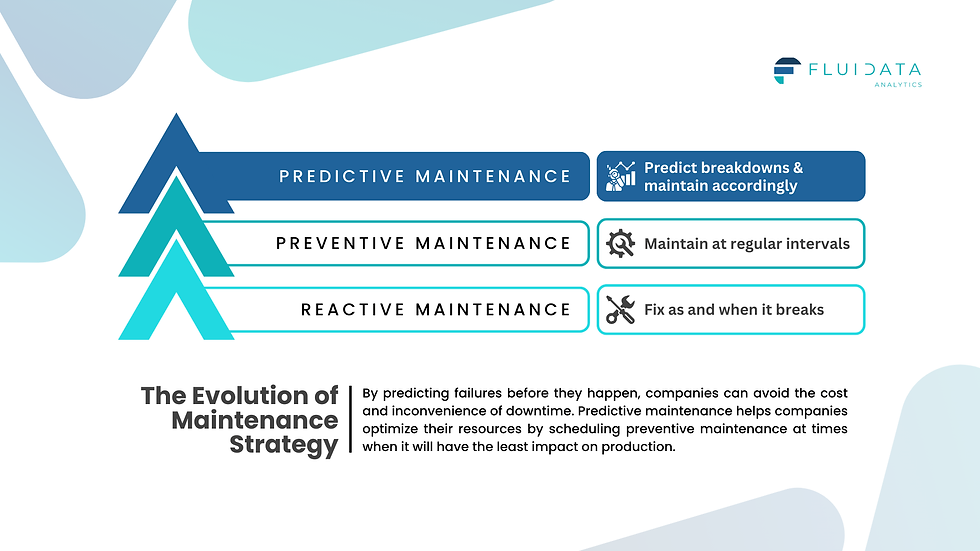
What is Reactive Maintenance? This occurs when a failure has already happened unexpectedly and needs to be resolved. This usually means increased downtime and lost productivity. Reactive maintenance is often the most disruptive and costly approach since it deals with issues only after they arise.
What is Preventive Maintenance? This refers to maintenance activities that are planned and executed at regular intervals, such as monthly maintenance of machinery. While preventive maintenance can help avoid unexpected failures, it can also incur unnecessary costs. Maintenance is performed regardless of whether there is an emerging issue, based on a predefined schedule that may not align with the actual condition of the equipment.
What is Predictive Maintenance? This is where the real innovation happens. Predictive maintenance leverages past performance data and information generated by IoT devices and sensors. By using machine learning, companies can analyze data-driven insights and real-time operating conditions to optimize when and how to execute maintenance. This approach helps avoid unnecessary repairs, optimizes the utilization of equipment, and drastically reduces downtime.
How Does Predictive Maintenance Work?
Predictive maintenance relies on various technologies including the Internet of Things (IoT), predictive analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI). Connected sensors gather data from assets such as machinery and equipment. This is collected at the edge or in the cloud in an AI-enabled enterprise asset management (EAM) or computerized maintenance management system (CMMS). AI and machine learning are used to analyze the data in real time to build a picture of the current condition of the equipment. Thereafter, triggering an alert if any potential defect is identified and delivering it to the maintenance team.
As well as providing defect warnings, advances in machine learning algorithms enable predictive maintenance solutions to make predictions about the future condition of equipment. These can be used to drive greater efficiency in maintenance-related workflows and processes such as just-in-time work order scheduling and labour and parts supply chains. Furthermore, the more data collected the more insights are generated and the better the predictions become. This can give businesses the confidence that their equipment are working optimally.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Benefits from a predictive maintenance strategy centre around anticipating equipment faults and failures, reducing maintenance and operating costs by optimizing time and resources, and improving the performance and reliability of equipment. Deloitte reported in 2022 that predictive maintenance can result in a 5-15% reduction in facility downtime and a 5-20% increase in labour productivity. Predictive maintenance also has a beneficial impact on operational sustainability by minimizing energy usage and waste.
Optimizing asset performance and uptime can reduce costs: Anticipatory warning of potential faults results in fewer breakdowns as well as reduced planned maintenance or unplanned downtime. Improved continuous condition visibility enhances the lifetime reliability and durability of equipment. The use of AI can more accurately forecast future operations. This benefit is paramount in a world where rising prices and unpredictable events like the pandemic and climate-related natural disasters expose the need for educated equipping of spare parts inventory, labour cost optimisation, and a lower environmental impact from operations.
Productivity can be increased: By reducing inefficient maintenance operations. Enabling a faster response to problems via intelligent workflows and automation, and equipping technicians, data scientists and employees across the value chain with better data with which to make decisions. The upshot is improved metrics such as mean time between failures (MTBF) and mean time to repair (MTTR), safer working conditions for employees, and revenue and profitability gains.
Predictive Maintenance Examples in Action
Oil and gas sector: Oil drilling puts enormous wear on assets and can lead to great risk and danger in the event of a failure. By monitoring oil temperature and the speed of gearboxes in drilling equipment, predictive maintenance has greatly improved safety and reduced maintenance costs by up to 38%.
Automotive industry: On assembly lines, spot-welding guns perform about 15,000 spot welds each per day. By connecting welding guns around the world and collecting their operational data, auto manufacturers can gather millions of data points, leading to unprecedented predictive accuracy on the condition and state of these assets.
Domestic appliance manufacturing: Vibration measurements of the drum rotation in the production of dryers have helped predict malfunctioning or breakdown. This predictive maintenance application has eliminated manufacturing defects by 33% and reduced consumer maintenance costs by 27%.
Railroad asset management: “Voids” occur when an empty space develops under a track leading to potential delay or even derailment. Recent innovation has led to cab-based systems that monitor a number of variables as they roll over the rails. This has led to improved void detection and an overall rise in customer safety.
Steel industry: Anomaly detection is being used to gather real-time readings of the vibration, rotational speed, and electrical current (amperes) in the cold-rolling equipment used in steel processing. This application has led to a 60% improvement in equipment lifetime and greatly reduced losses due to downtime and delays.
Takeaway
Predictive maintenance is revolutionizing the way businesses approach equipment maintenance, offering a proactive, data-driven solution to reduce downtime and costs. By harnessing the power of advanced analytics and IoT technology, companies can achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and operational resilience. As the industrial landscape continues to evolve, predictive maintenance stands out as a vital strategy for future-proofing operations and maintaining a competitive edge.
Reach out to us at hello@fluidata.co


Comments